Technical Column
What is cemented carbide? See the specialties and grades.
Contents
- 1 What is cemented carbide?
- 2 Characteristics of cemented carbide
- 3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Cemented Carbides
- 4 Composition of Cemented Carbide
- 5 Contributes to society in a wide range of applications
- 6 Types of cemented carbide
- 7 Please contact us for material selection and processing of cemented carbide.
What is cemented carbide?
Cemented carbide is an alloy composed of hard metal carbide and iron based metal.
The most typical composition of cemented carbide is WC-Co alloy.
Made by sintering compound of WC and Co powder at 1,400 degrees celsius, cemented carbide possess hardness following diamond and high modulus of elasticity. Due to such high hardness and elastic modulus, cemented carbide is used for machining tools and press dies that require wear resistance.
Characteristics of cemented carbide
Other than cemented carbide, high speed tool steel is also a common material for working tools.
We will explain below the characteristics of cemented carbide in comparison with high speed tool steel.
Cemented carbide has higher values in hardness, elastic modulus, compressive strength, thermal conductivity and specific gravity compared with high speed tool steel, while values such as thermal expansion coefficient, impact strength and fracture toughness are lower.
However, the characteristics of cemented carbides are not all the same. As cemented carbides are manufactured by powder metallurgy, it is possible to produce alloys with a variety of properties through a combination of material selection. Therefore, it is possible to manufacture tools that match the characteristics of the workpiece.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cemented Carbides
Advantages of Cemented Carbides
- Cemented carbides are characterized by their extreme hardness. Compared with HSS and die steel, cemented carbides have higher wear resistance and can extend the service life of mold parts, jigs, and other components. Longer service life reduces the frequency of maintenance and improves productivity.
- As cemented carbides are not easily deformed due to high modulus of elasticity and compressive strength, they can be machined for mold parts with high dimensional accuracy.
- Cemented carbides can be recycled and are environment-friendly materials.
Disadvantages of Cemented Carbides
- Because cemented carbides are extremely hard, they are also brittle, and depending on the grade may chip easily or be susceptible to impact.
- Cemented carbides could be expensive due usage of rare metals such as tungsten carbide and cobalt.
- As cemented carbide is second only to diamond in terms of hardness, it requires special tools and machines for processing such as diamond-abrasive grinding wheels, grinders, and electric discharge machines.
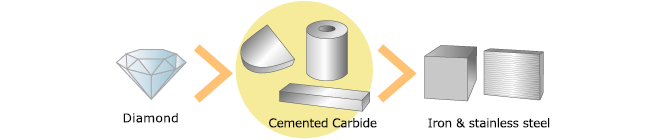
Cemented carbide is an extremely hard metal.
It is harder than iron and stainless steel, and the hardness is next to diamond.
Also, it weighs twice as much as iron, which is almost the same as gold.
Not only is it hard, but it also has excellent strength and elasticity.
Decrease in hardness at high temperatures is also small, and is not easily worn.
Because of those reasons, it is used for metal processing tools and dies.
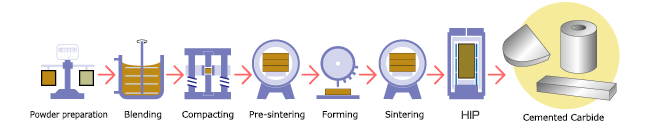
Composition of Cemented Carbide
Cemented Carbide is not a natural metal, but an artificially made alloy.
It is composed of tungsten carbide (WC) and cobalt (Co).
Tungsten carbide has a high melting point (2900 degrees in Celsius,) and cannot be melted and made like iron.
Therefore, cemented carbide is manufactured by sintering and hardening blended powder at high temperatures from 1300 to 1500 degrees celsius.
Cobalt is used as a binder at that time.
Most of the tungsten is from China, and others places include Russia and South Korea.
Cobalt can be mined as ore from Finland, Canada, Australia and Congo.
Contributes to society in a wide range of applications
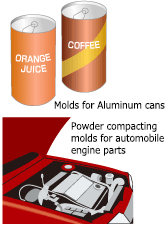
Given its hardness and strength, cemented carbide is used in cutting tools for metal processing such as drills, milling cutters, and lathes.
It is also used in molds for aluminum cans used for canned drinks, powder molding dies for making sintered automobile engine parts, and recently, molds for parts used in electronics like mobile phones.
It is also used for crushing hard rock in shield tunnelling and for cutting the surface of asphalt roads.
Due to its excellent properties, cemented carbide is used in a wide range of industrial fields such as manufacturing and public works for infrastructure development.
Types of cemented carbide
Function of cemented carbide can be broadly divided into 2 categories: cutting and wear resistance.
Cemented carbide for cutting can be divided into 3 types, P type (for steel), M type (general purpose), and K type (for cast iron), depending on the material of the workpiece. There are different types of wear-resistant cemented carbides, finely classified according to binder phase type, WC grain size and hardness. As a cemented carbide manufacturer, we developed grades focusing on specific issues, possess a wide variety of grades in order to meet the diverse demands of our customers.
Please contact us for material selection and processing of cemented carbide.
We selected and processed a large number of cemented carbides.
Among them, we have proposed solutions for customer’s various problems by selecting and processing the most suitable materials.
We will be able to select the appropriate cemented carbide for the intended application and perform the appropriate processing.
If you have any problems with the use of cemented carbide, please feel free to contact us.
Frequently asked questions
-
What is the difference between cemented carbide and ceramics?
The hardness of ceramics approaches that of diamond, the hardest mineral on earth. If the hardness of diamond is 10, ceramics exhibit a hardness of 9 or higher, which is harder than tungsten and other hard metals. The difference in composition also results in a heavier weight in the case of cemented carbides. However, cemented carbides can be made with various characteristics depending on tungsten carbide (WC) particle size, the amount of bonding material, and additives, so it is possible to select the most suitable grade for the application from a wide range of available grades.
-
What is the difference between cemented carbide and cermet?
Both cemented carbide and cermet are composite materials made by mixing and sintering carbide or nitride powders with a metallic binder.
However, whereas cemented carbides are made of tungsten carbide (WC), the main component, bonded mainly with cobalt (Co) and nickel (Ni),
Cermet is made by bonding titanium compounds such as titanium carbide (TiC) and titanium carbide nitride (TiCN) with nickel (Ni) and cobalt (Co).
In other words, the difference between cemented carbide and cermet is the main component. -
What is the difference between cemented carbide and HSS?
Cemented carbide is an alloy with high hardness, heat resistance and strength. HSS, on the other hand, generally has relatively lower strength and heat resistance, but has higher impact resistance.
As their raw materials and manufacturing methods differ, there is a significant difference in costs between the two materials.
Selecting the suitable material is recommended though considering the application and the timing of replacement after installation.
-
What are the weaknesses of cemented carbides?
Compared to general iron alloys, cemented carbide has lower toughness, which may cause chipping or peeling of the cutting edge.
In addition, as the relative density is about twice that of iron, the heavier weight of cemented carbide may be a disadvantage. -
What causes cemented carbide to crack?
Compared to metal materials, cemented carbide materials have a different thermal expansion coefficient. For this reason, cracks may occur in shrink/cooling-fitted products when the operating temperature is significantly higher (lower) than the designed value. When using cemented carbides with high hardness, problems such as cracking may occur by high impact, so the required fracture toughness value should also be carefully considered.
-
What kind of cemented carbide is used as cutting tools?
The material of cemented carbide to be selected depends on the workpiece and its thickness, etc. In general, for use as a cutting tool, ultrafine grain cemented carbide, which consists of ultrafine tungsten carbide (WC) particles, is often selected to increase cutting ability and to prevent chipping.
-
What are the advantages of using cemented carbide tools?
As cemented carbide is characterized by its resistance to loss of hardness at high temperatures, its performance is not easily deteriorated even when used for machining at high speed that cause tools to have high temperatures.
-
What is the hardness of cemented carbides?
Generally, hardness can range from HRA88 to HRA92.
Higher hardness increases wearing resistance, but decreases impact resistance making it more prone to chipping. -
What is the main component of cemented carbide?
The main component is tungsten carbide (WC), which becomes cemented carbide after bonding with metallic binders such as cobalt and nickel.
Additives such as chromium (Cr) are added to these alloys to create cemented carbides with various characteristics.
-
Catalog
We will provide high value-added cemented carbide with the achievements and know-how cultivated so far.
Download -
Consultation and Inquiry
We solve your problems by providing integrated solutions from material selection/development to precision machining and provision of finished products.
Contact us -
FAQ
We have posted the contents of many inquiries from customers in the past.
Click for details
